Unix-like 操作系统中,程序的 stderr、exit status,以及 Go 语言如何捕捉命令执行错误实例。

Table of Contents
在一次开发中,需要用 Go 语言的 os/exec 包执行命令、捕获成功与否。
本文在此梳理 Unix-like 操作系统中进程对错误信息的处理,并提供了几组实例。
1 stderr
1.1 standard stream
stderr 即 standard error,定义于POSIX标准中,是进程用来输出错误信息的文件描述符。
在Linux中,有3种标准流(standard stream),分别为stdin,stdout, stderr。
这些标准流也被当做文件看待,因此也有对应的文件描述符做标识。
| 文件描述符 | 名称 |
|---|---|
| 0 | stdin |
| 1 | stdout |
| 2 | stderr |
如此设计,一个进程的错误输出和标准输出可以分别被处理。
1.2有stderr输出意味着程序失败吗?
Tip:
我们最终目的是使用 os/exec 捕捉错误信息。 所以需要了解到,有错误输出并不一定意味着程序发生了致命错误。
比如 ffmepg 中编解码可能遇到一些被容忍的错误,并输出 stderr 异常信息。但并不意味着该程序执行失败。
1.3输出重定向
我们在shell中执行命令,可以使用 > 将输出流重定向,比如到文件中。
经常见到的 2>&1 ,即将 stderr 重定向到 stdout 中, 并保持原有 stdout 输出。
实例:
ls 的重定向输出
ls 存在的文件时,返回标准输出 stdout,反之输出到 stderr。
# 实验目录总览
➜ ls -lh
total 0
-rw-rw-r-- 1 pi pi 0 7 月 31 17:38 1.txt
# stdout
➜ ls -lh 1.txt 1>/dev/null
➜ ls -lh 1.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 pi pi 0 7 月 31 17:38 1.txt
# stderr
➜ ls -lh 2.txt
ls: cannot access '2.txt': No such file or directory
➜ ls -lh 2.txt 1>/dev/null
ls: cannot access '2.txt': No such file or directory
➜ ls -lh 2.txt 2>/dev/null
# 重定向 2>&1, 一并输出到文件
➜ ls -lh 2.txt > result.txt 2>&1
# 查看得到的文件内容
➜ cat ./result.txt
ls: cannot access '2.txt': No such file or directory
2 status code
status code 是Linux中进程执行返回的退出代码,用于标志成功与否。为0时,标志成功执行,非零表示发生错误。
2.1错误捕捉
在shell中可以使用 $? 来捕捉上次命令的退出状态。
# status code = 0
➜ ls -lh 1.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 pi pi 0 7 月 31 17:38 1.txt
➜ echo $?
0
# status code != 0
➜ ls -lh 2.txt
ls: cannot access '2.txt': No such file or directory
➜ echo $?
2在一些多功能的shell套件中,如oh-my-zsh,可配置直接将 status code 以各种形式快捷显示出来,如:
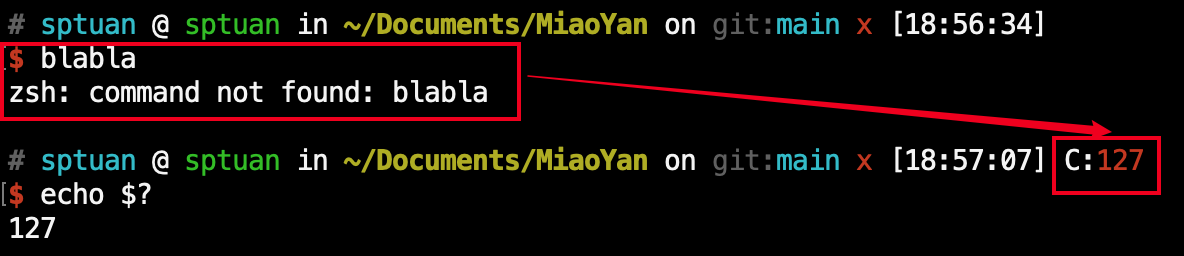
2.2常见错误约定
一般情况为0时,标志成功执行,非零表示发生错误。
具体可以参考 Appendix E. Exit Codes With Special Meanings - Advanced Bash-Scripting Guide
3 Go os/exec错误捕捉
假设情景为,我们需要使用Go语言执行 nginx -s reload 指令,并捕捉是否成功。
os/exec 包为我们提供了健壮的外部命令调用。包内的 cmd 能够让我们自行指定stdin,stdout,stderr的IO输入输出。
为了实现简单,我们可以使用 CombinedOutput() 将stdout,stderr组合作为输出(即2>&1),然后捕获 cmd 自身的错误或程序输出的异常 status code。
实例Go代码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os/exec"
)
func main() {
ReloadNginx()
}
func ReloadNginx() {
cmd := exec.Command("/usr/sbin/nginx", "-s", "reload")
output, err := cmd.CombinedOutput()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("[ERROR] Reload nginx failed:", err)
fmt.Println("[ERROR] Reload nginx output:", string(output))
return
}
fmt.Println("[INFO] Reload nginx success:", string(output))
}
失败时的捕获
➜ sudo ./main
[ERROR] Reload nginx failed: exit status 1
[ERROR] Reload nginx output: nginx: [alert] could not open error log file: open()"/var/log/nginx/error.log" failed (13: Permission denied)
2022/07/31 19:33:50 [warn] 2390199#2390199: the "user" directive makes sense only if the master process runs with super-user privileges, ignored in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf:1
2022/07/31 19:33:50 [notice] 2390199#2390199: signal process started
2022/07/31 19:33:50 [error] 2390199#2390199: open()"/run/nginx.pid" failed (2: No such file or directory)
成功时的输出
➜ sudo ./main
[INFO] Reload nginx success:
4 小结
梳理了 stderr exit status,写了个简单的错误捕捉例程。
对于我们自己编写的程序或者shell脚本,只要遵守上述的输出和返回码,就可以方便地被第三方调用和捕获状态。


我的这套 wordpress 实在是太老旧了,markdown 写的笔记发表在上面展示得一塌糊涂,排版非常痛苦。
真应该找个时间修整一番